Contents
- 1 TL;DR
- 2 Introduction to Blockchain in Supply Chain
- 3 Capabilities Before Getting Started
- 4 Conclusion: Future Prospects of Blockchain in Supply Chain
TL;DR
- This article talks about blockchain in supply chain
- The digital concept of blockchain records transactions in a shared and distributed record system rather than having a single central party own them.
- This decentralised system’s details ensure a secure and immutable transaction record. Blockchain can guarantee product authenticity, diminish fraud, and cultivate trust among supply chain stakeholders.
- Successfully implementing blockchain in supply chain necessitates integrating IoT, establishing a system for recording transactional data, standardising data, and defining success metrics.
- With its potential to introduce transparency, traceability, and trust, blockchain stands poised to revolutionise future supply chain operations.
Blockchain technology, best known as the technology behind cryptocurrencies, is reshaping various industries by bringing transparency, security, and efficiency. One such industry where blockchain is making significant inroads is supply chain management. This blog post will examine how blockchain in supply chain enhances transparency and traceability in operations and delve into its role in ensuring product authenticity, reducing fraud, and improving customer trust. Additionally, we’ll will also discuss the capabilities required for effective implementation.
Introduction to Blockchain in Supply Chain
Understanding Blockchain Technology
Blockchain employs a technological concept where a series of decentralised network nodes record transactions and then compare their records against all others to identify discrepancies. Every block in the chain houses multiple transactions, which vary in use cases. Every node’s ledger includes that transaction record whenever a new transaction happens on the blockchain. All participants can see every transaction, and no one can alter any transaction retrospectively as a result a blockchain is high transparent and secure
Explaining to Different Audiences
What does this even mean? Let’s explain it with increasing levels of complexity:
For an 11-year-old
Think of you and your friends keeping track of card trades in a special notebook. You lock each entry with a magic key that everyone owns. Once locked, no one can change it – not even by mistake. If anyone tries, everyone will know!
For a recent graduate
Blockchain acts like a digital notebook. You add information, and a unique digital ‘seal’ secures it. If anyone tries to change the info, the seal breaks for everyone to see. That’s why altering or deleting data is nearly impossible – it’s like a secret security guard!
For a supply chain expert
Blockchain links each transaction or ‘block’ to the ones around it using intricate mathematical codes or ‘hashes.’ If a block alters, the links break, and the whole network sees it. This makes changing a block nearly impossible, as you’d need to change every following block simultaneously. Every network node cross-checks others, ensuring only genuine data spreads.
A computer science major
A blockchain’s block houses transactions, a timestamp, and a cryptographic hash from the previous block. This chaining makes blockchain resistant to data modification. If someone alters a record, it disrupts the chain’s hashes, revealing a network discrepancy. With the consensus model, changes need the majority’s approval. This renders blockchain a secure, tamper-evident structure.
Comparing Blockchain with Legacy Centralised Ledgers
Blockchain technology represents a paradigm shift from traditional record keeping. A single, trusted entity maintains the record of all transactions in a centralised ledger system. This central entity has the power to add, modify, or delete entries, which can lead to transparency and trust issues. Information asymmetry and lack of transparency can occur in such systems, leading to potential disputes, fraud, and inefficiencies.
On the other hand, a blockchain is a decentralised or distributed (depending on implementation) ledger where no single party has control. Every node in the network has access to the entire blockchain, and therefore all transactions are transparent to all members matched with a consensus-based conformity checker; once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This eliminates the possibility of fraud, errors, or inconsistencies in centralised ledgers. The enhanced security, transparency, and trust blockchain offers make it an attractive alternative to traditional, centralised ledger systems in supply chain management.
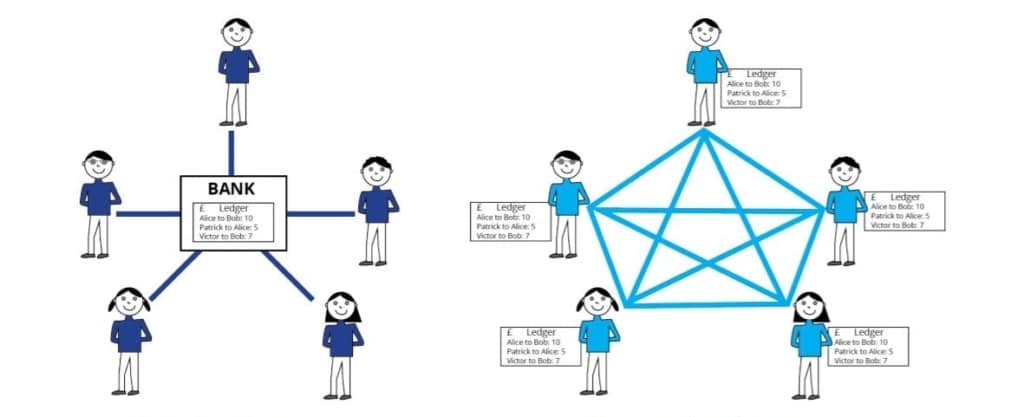
I like this simple diagram of how blockchain can be applied in the banking industry. Notice a few things:
- Notice how in the centralised model on the left, a central body has unchallenged authority to record whatever it wants? The result of an error or a bad actor could lead to many issues.
- In the distributed model on the right, this authority is shared at the cost of processing power.
Examples of how blockchain is used in other industries
Blockchain has been successfully adopted across various sectors beyond its original application in cryptocurrencies. For example:
- The finance industry uses blockchain to simplify and secure payment transactions. Think about Bitcoin or the plethora of other cryptocurrencies.
- In the healthcare sector, it is used for secure and transparent record-keeping. Check out these examples of solutions in this space
- In real estate, it aids in the simplification of property transactions by removing the need for intermediaries. See how blockchain is transforming real estate.
Impact of Blockchain in Supply Chain
Blockchain’s decentralisation, transparency, and security offer significant benefits when applied to supply chain management. It provides traceability and transparency that was previously difficult, if even possible, to achieve. By offering a secure and immutable record of transactions, blockchain technology can help establish trust, ensure authenticity, and reduce fraud.
Ensuring Product Authenticity to End Customers
Product counterfeiting and adulteration are rampant in various sectors, from pharmaceuticals to luxury goods. Blockchain technology can help tackle this issue by providing a secure and tamper-proof product history record, therefore ensuring product authenticity. Consumers can verify the product’s origin, journey through the supply chain, and authenticity, fostering trust in the product and the brand.
Traceability through a supply chain has applications for end customers who demand traceability for sustainable sourcing. Imagine if a clothing brand whose image is based on sustainable sourcing can guarantee to end customers that an item of clothing comes from sustainable sources or fair trade organisations.
Reducing Fraud and Increasing Trust
Blockchain’s immutable and transparent nature can significantly reduce fraud in the supply chain. It eliminates the risk of forged documentation and tampered records, common tactics in supply chain fraud. By providing a verifiable and unalterable record of transactions, blockchain can foster trust among all supply chain stakeholders, including suppliers, manufacturers, retailers, and consumers.
Capabilities Before Getting Started
Internet of Things (IoT)
While not always true, the Internet of Things (IoT) enables blockchain implementation in supply chain management. IoT devices can provide real-time data about a product’s status and location, which can be recorded securely on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and traceability.
For example, an IoT device that tracks location and temperature control for a healthcare product could report directly back to a blockchain without requiring manual record maintenance.
A System to Record Transactional Data
An efficient system for recording transactional data is critical for the successful implementation of blockchain in the supply chain. This system must capture necessary transaction details, such as date, time, location, participants, and line items, and record them on the blockchain accurately and securely.
Standardised Data
The effectiveness of blockchain in enhancing supply chain transparency also depends on the standardisation of data. Establishing standards for data formatting, recording, and exchange is necessary to ensure that the data recorded on the blockchain is consistent, accurate, and meaningful.
A Success Metric
Finally, to evaluate the success of blockchain implementation in the supply chain, it is necessary to define appropriate success metrics before implementation. As a part of a broader vision, a company needs to have a clear use case/idea of what problem is being solved, as implementation takes some effort, especially for established businesses, and a north star is often needed. These metrics could be related to improved traceability, reduction in fraud, increased trust, or enhanced operational efficiency.
Conclusion: Future Prospects of Blockchain in Supply Chain
Blockchain technology holds immense promise for the future of supply chain management. Its potential to enhance transparency, improve traceability, ensure product authenticity and foster stakeholder trust positions it as a game-changer in supply chain operations. As more and more companies utilise blockchain in their operations, we expect to see more transparent, efficient, and secure supply chains.

