Contents
TL;DR
- Psychological safety is essential for high performance and innovation in the workplace.
- By rethinking traditional performance management practices through the lens of psychological safety, organizations can foster environments that encourage open communication, risk-taking, and continuous learning.
- Leadership practices, feedback cultures, and appropriate metrics are crucial to building and sustaining psychological safety.
- Overcoming challenges and balancing accountability with psychological safety are vital for success.
- Google’s seminal Project Aristotle found that the critical component of a high-performance team was psychological safety.
In today’s fast-paced and ever-evolving work environment, psychological safety and performance management concepts are at the forefront of organizational success. Amy Edmondson coined the term “psychological safety,” which has become integral to understanding how high-performing teams operate and thrive. Establishing psychological safety is foundational for effective performance management and cultivating environments where innovation and engagement flourish.
Understanding Psychological Safety
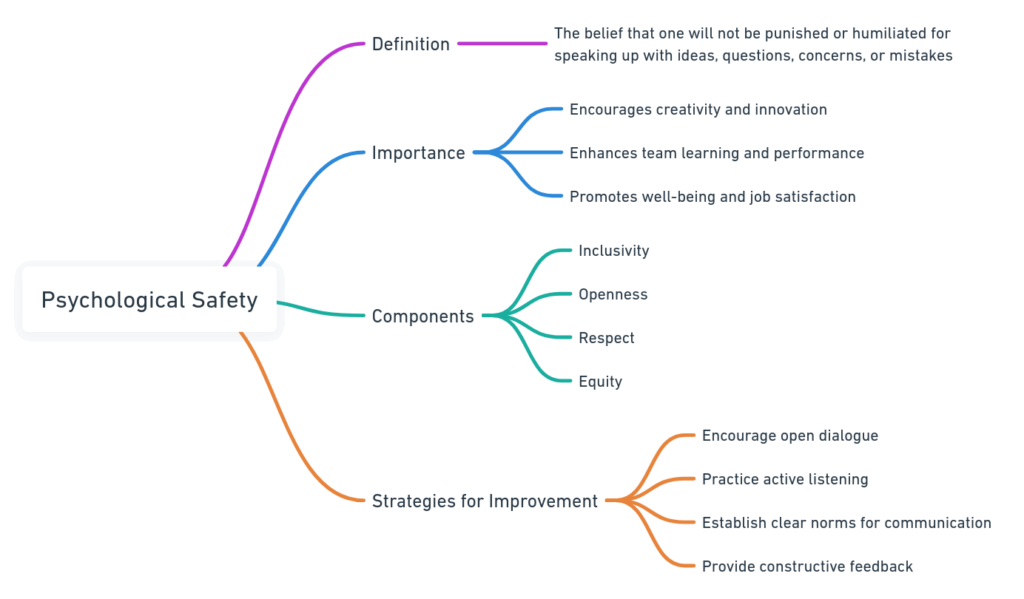
Definition and Key Components
Psychological safety refers to an individual’s perception of the consequences of an interpersonal risk. It’s about feeling safe to express oneself without fear of negative consequences to self-image, status, or career. This concept differs from trust, which focuses on confidence in others’ competence and reliability.
Psychological safety in the workplace is defined as an environment where employees feel secure in taking risks, asking questions, or making mistakes without fear of punishment or ridicule. This concept is vital for fostering a culture of open communication, innovation, and continuous learning, as it encourages individuals to share their ideas and concerns freely. A psychologically safe workplace supports team collaboration and individual well-being, contributing to overall organizational success.
The Importance of Psychological Safety in the Workplace
Extensive research by Mckinsey underscores the significance of psychological safety in enhancing team performance and fostering an innovative culture. Case studies across various industries reveal that teams with high levels of psychological safety are more likely to leverage diverse ideas, leading to breakthrough innovations and solutions.
For many, this can translate as simply having the right to fail when trying new ideas, learning, taking professional risks or transforming without fear of punishment.
The Intersection of Psychological Safety and Performance Management
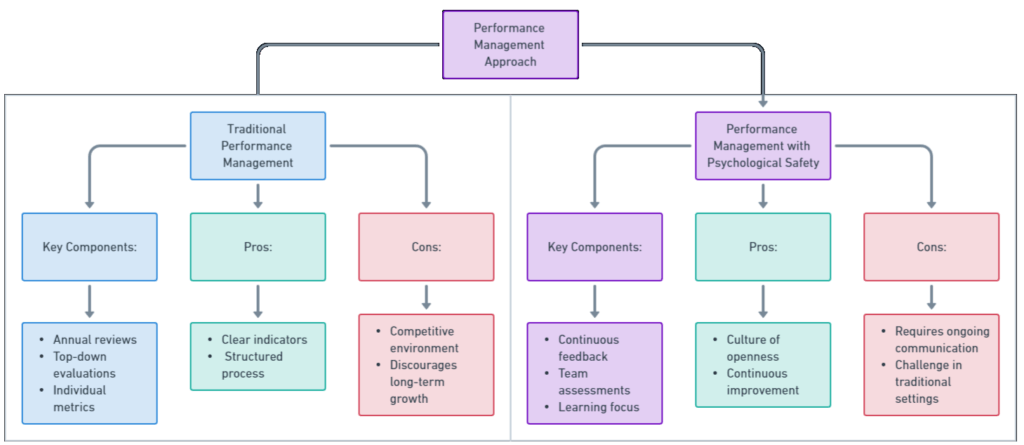
Traditional Performance Management Paradigm
- Traditional performance management often revolves around annual reviews and rankings, which can stifle creativity and hinder open communication.
- These conventional methods can limit growth and development opportunities and may need to be revised to support modern teams’ dynamic needs adequately.
Performance Management through the Lens of Psychological Safety
- Incorporating psychological safety into performance management transforms it from a rigid evaluation process to a dynamic growth-oriented system.
- Strategies include fostering open dialogue, emphasizing learning opportunities, and integrating continuous feedback mechanisms.
Strategies Building Psychological Safety
- Leadership Practices: Leaders play a pivotal role in establishing a psychologically safe environment by demonstrating vulnerability, encouraging open participation, and setting clear expectations. These practices enhance team cohesion and pave the way for more effective performance management.
- Practice active listening
- Establish clear norms for communication
- Focus on learning outcomes and not punitive measures when mistakes are made
- Encourage open dialogue: Adopting a culture where feedback is viewed as a mechanism for learning and growth is crucial. These techniques can significantly contribute to a team’s psychological safety and overall performance.
- Regular, informal check-ins
- Constructive feedback sessions
- Lessons learnt sessions after key projects
- Measuring Psychological Safety and Performance Outcomes: Utilizing tools and metrics to assess psychological safety within teams allows organizations to make informed decisions and link these measures to performance outcomes. This data-driven approach facilitates a deeper understanding of the relationship between psychological safety and team effectiveness.
- Employee Surveys: Customizable surveys focusing on trust, openness, and comfort in taking risks.
- 360-Degree Feedback Tools: Collecting feedback from peers, subordinates, and superiors to assess interpersonal dynamics and team safety.
- Engagement and Well-being Platforms: Tools that measure overall employee engagement and well-being can indirectly indicate the level of psychological safety.
- Performance Metrics Analysis: Analyzing patterns in performance data can help identify areas where a lack of psychological safety may be affecting outcomes.
- AI-Powered Sentiment Analysis: Leveraging AI to analyze communication patterns and sentiments in team interactions can provide insights into the team’s psychological safety.
Challenges and Considerations in Promoting Psychological Safety
- Navigating Resistance and Skepticism: Fostering a psychologically safe workplace can cause resistance. Overcoming skepticism involves communicating the benefits and demonstrating the tangible impact on performance and engagement.
- Balancing Accountability with Psychological Safety: Maintaining high standards and accountability while ensuring a psychologically safe environment requires a nuanced approach. Successful organizations navigate this balance by emphasizing learning from failures and fostering mutual respect.
- Organizational Environment: The extent to which a culture of psychological safety is fostered often hinges on the team’s operational setting. For instance, a consulting group interacting closely with a client’s executive team may have less leeway for errors than a research and development team dedicated to idea exploration.
A Case Study: Project Aristotle
Project Aristotle was an initiative by Google to study and understand what makes a team effective at Google. This research project, conducted over several years, involved analyzing data from hundreds of Google’s teams to identify the dynamics contributing to team success. Here are the key findings of Project Aristotle:
- Psychological Safety: The most important factor that emerged from the research was psychological safety, a shared belief among team members that the team is safe for interpersonal risk-taking. This means team members feel confident they won’t be embarrassed, rejected, or punished for speaking up with ideas, questions, concerns, or mistakes.
- Dependability: Team members rely on each other for high-quality work on time. Dependability ensures that everyone meets the team’s expectations regarding performance and deadlines, creating a reliable working environment.
- Structure and Clarity: Effective teams have clear goals, roles, and execution plans. This includes knowing what is expected of team members individually, how they fit into the larger team, and understanding the team’s overarching objectives.
- Meaning of Work: Each team member personally values their work. When team members find their work meaningful, they are more likely to be engaged and committed to the team’s success.
- Impact of Work: Team members believe their work matters and creates change. Knowing that one’s work significantly contributes to the team or organization can boost motivation and performance.
Project Aristotle’s insights emphasize that the “who” part of a team is not as critical as the “how” the team works together. It highlighted the importance of soft skills, communication, and emotional intelligence in team dynamics, suggesting that creating the right environment is vital to team effectiveness. These findings have implications beyond Google, offering valuable lessons for organizations striving to build successful teams.
Conclusion
Integrating psychological safety into performance management represents a paradigm shift towards more adaptive and resilient organizational cultures. As the future of work continues to evolve, the need for environments that support open dialogue, risk-taking, and continuous learning becomes increasingly apparent. Leaders and HR professionals are called upon to champion these principles, recognizing that the path to a high-performance team or organization is built on a foundation of psychological safety.